The notation follows `A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition', Rabiner, 1989. More...
Functions | |
| template<int States, class Btype , class Otype > | |
| std::tr1::tuple< double, TooN::Vector < Btype::NumParameters > , TooN::Matrix < Btype::NumParameters > > | forward_algorithm_hessian (TooN::Matrix< States > A, TooN::Vector< States > pi, const Btype &B, const std::vector< Otype > &O, bool compute_deriv=1, bool compute_hessian=1) |
| template<int States, class Btype , class Otype > | |
| double | forward_algorithm (TooN::Matrix< States > A, TooN::Vector< States > pi, const Btype &B, const std::vector< Otype > &O) |
| template<int States, class Btype , class Otype > | |
| std::pair< double, TooN::Vector < Btype::NumParameters > > | forward_algorithm_deriv (TooN::Matrix< States > A, TooN::Vector< States > pi, const Btype &B, const std::vector< Otype > &O) |
| template<int States, class Btype , class Otype > | |
| std::vector< std::tr1::array < double, States > > | forward_algorithm_delta (TooN::Matrix< States > A, TooN::Vector< States > pi, const Btype &B, const std::vector< Otype > &O) |
| template<int States, class Btype , class Otype > | |
| void | forward_algorithm_delta2 (TooN::Matrix< States > A, TooN::Vector< States > pi, const Btype &B, const std::vector< Otype > &O, std::vector< std::tr1::array< double, States > > &delta) |
| template<int States, class Btype , class Otype > | |
| std::pair< std::vector < std::tr1::array< double, States > >, std::vector < std::tr1::array< double, States > > > | forward_backward_algorithm (TooN::Matrix< States > A, TooN::Vector< States > pi, const Btype &B, const std::vector< Otype > &O) |
| template<class A , class Rng > | |
| int | select_random_element (const A &v, const double scale, Rng &rng) |
| template<int N, class Rng > | |
| int | sample_unscaled_log (std::tr1::array< double, N > a, Rng &rng) |
| template<int States, class StateType , class Rng > | |
| std::vector< StateType > | backward_sampling (TooN::Matrix< States > A, const std::vector< std::tr1::array< double, States > > &delta, Rng &rng) |
Detailed Description
The notation follows `A tutorial on hidden Markov models and selected applications in speech recognition', Rabiner, 1989.
Function Documentation
| std::tr1::tuple<double, TooN::Vector<Btype::NumParameters>, TooN::Matrix<Btype::NumParameters> > forward_algorithm_hessian | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| TooN::Vector< States > | pi, | ||
| const Btype & | B, | ||
| const std::vector< Otype > & | O, | ||
| bool | compute_deriv = 1, |
||
| bool | compute_hessian = 1 |
||
| ) |
The forward algorithm is defined as:
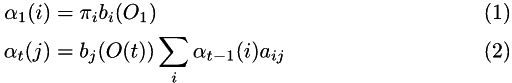
And the probability of observing the data is just:
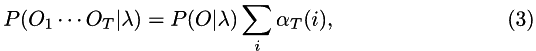
where the state, 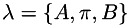 .
.
All multipliers are much less than 1, to 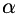 rapidly ends up as zero. Instead, store the logarithm:
rapidly ends up as zero. Instead, store the logarithm:
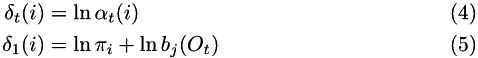
and the recursion is:
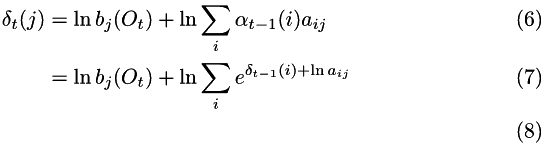
including an arbitrary constant,  gives:
gives:
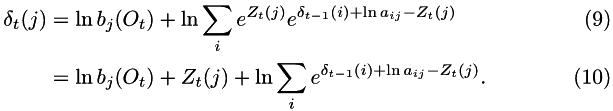
In order to prevent a loss of scale on the addition:
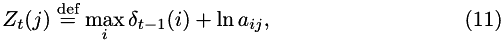
so the largest exponent will be exactly 0. The final log probability is, similarly:
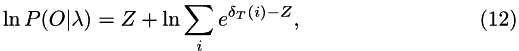
Z can take any value, but to keep the numbers within a convenient range:

For computing derivatives, two useful results are:
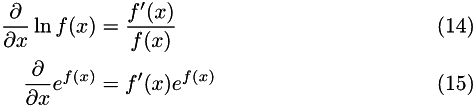
There are M parameters of B, denoted  . The derivatives of P are:
. The derivatives of P are:
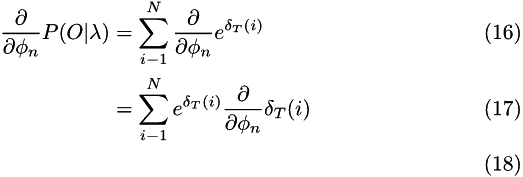
Taking derivatives of 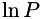 and rearranging to get numerically more convenient results gives:
and rearranging to get numerically more convenient results gives:
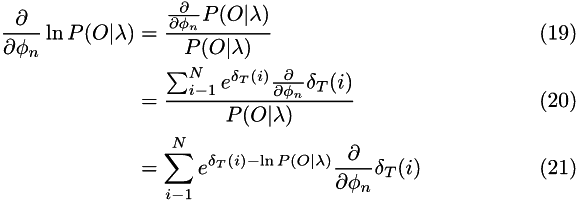
The derivarives of 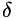 are:
are:
![\begin{align} \gdef\dtj{\delta_T(j)} \PD{\dtj}{\en} &= \DD \ln \left[ b_j(O_t) \SSum e^{\delta_{t-1}(i) + \ln a_{ij}} \right] \\ &= \DD \left[ \ln b_j(O_t) \right] + \frac{\SSum \DD e^{\delta_{t-1}(i) + \ln a_{ij}}}{\SSum e^{\delta_{t-1}(i) + \ln a_{ij}}}\\ \underset{\text{\tt diff\_delta[t][j]}}{\underbrace{\PD{\dtj}{\en}}} &= \underset{\text{\tt B.diff\_log(j, O[t])}}{\underbrace{\DD \left[ \ln b_j(O_t) \right]}} + \frac{\overset{\text{\tt sum\_top}}{\overbrace{\SSum e^{\delta_{t-1}(i) + \ln a_{ij} - Z_t(j)} \DD \delta_{t-1}(i)}} }{\underset{\text{\tt sum}}{\underbrace{\SSum e^{\delta_{t-1}(i) + \ln a_{ij} -Z_t(j)}}}}, \end{align}](form_21.png)
with 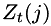 as defined in forward_algorithm.
as defined in forward_algorithm.
For computing second derivatives, with  yielding column vectors, two useful results are:
yielding column vectors, two useful results are:
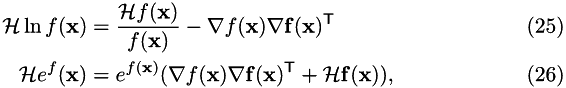
therefore:
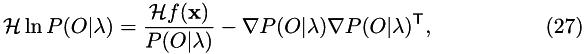
and:
![\begin{equation} \Hess P(O|\lambda) = \sum_i e^{\delta_t(i) - \ln P(O|\lambda)}\left[ \Grad\delta_t \Grad\delta_t\Trn + \Hess \delta_t\right]. \end{equation}](form_25.png)
Define 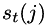 as:
as:
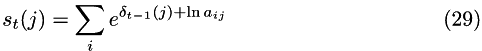
so that:
The derivatives and Hessian recursion are therefore:
![\begin{align} \Grad \delta_t(j) &= \Grad\ln b_j(O_t) + \frac{\Grad s_t(j)}{s_t(j)} \\ \Hess \delta_t(j) &= \Hess\ln b_j(O_t) + \frac{\Hess s_t(j)}{s_t(j)} - \frac{\Grad s_t(j)}{s_t(j)}\frac{\Grad s_t(j)}{s_t(j)}\Trn.\\ &= \underset{\text{\tt B.hess\_log(j, O[t])}}{\underbrace{\Hess\ln b_j(O_t)}} + \frac{ \overset{\text{\tt sum\_top2}}{ \overbrace{ \sum_i e^{\delta_{t-1}(j) + \ln a_{ij} - Z_t(j)}\left[\Hess\delta_{t-1}(i) + \Grad\delta_{t-1}(i)\Grad\delta_{t-1}(i)\Trn\right]}} }{\text{\tt sum}} - \frac{\text{\tt sum\_top sum\_top}\Trn}{\text{\tt sum}^2} \end{align}](form_29.png)
- Parameters:
-
A A: State transition probabilities. pi 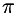 : initial state probabilities.
: initial state probabilities. O O or I: the observed data (ie the images). B 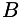 : A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
: A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters. compute_deriv Whether to compute the derivative, or return zero. compute_hessian Whether to compute the Hessian, or return zero. This implies compute_deriv.
- Returns:
- the log probability of observing all the data, and the derivatives of the log probability with respect to the parameters, and the Hessian.
Definition at line 134 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References ln().
Referenced by forward_algorithm_deriv(), sampled_background_spot_hessian2(), and sampled_background_spot_hessian_FAKE().
{
using namespace TooN;
using namespace std;
using namespace std::tr1;
if(compute_hessian == 1)
compute_deriv=1;
static const int M = Btype::NumParameters;
int states = pi.size();
//delta[j][i] = delta_t(i)
vector<array<double, States> > delta(O.size());
//diff_delta[t][j][n] = d/de_n delta_t(j)
vector<array<Vector<M>,States > > diff_delta(O.size());
//hess_delta[t][j][m][n] = d2/de_n de_m delta_t(j)
vector<array<Matrix<M>,States > > hess_delta(O.size());
//Initialization: Eqn 19, P 262
//Set initial partial log probabilities:
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
{
delta[0][i] = ln(pi[i]) + B.log(i, O[0]);
if(compute_deriv)
diff_delta[0][i] = B.diff_log(i, O[0]);
if(compute_hessian)
hess_delta[0][i] = B.hess_log(i, O[0]);
}
//Perform the recursion: Eqn 20, P262
//Note, use T and T-1. Rather than T+1 and T.
for(unsigned int t=1; t < O.size(); t++)
{
for(int j=0; j < states; j++)
{
double Ztj = -HUGE_VAL; //This is Z_t(j)
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
Ztj = max(Ztj, delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]));
double sum=0;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum += exp(delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]) - Ztj);
delta[t][j] = B.log(j, O[t]) + Ztj + ln(sum);
if(compute_deriv)
{
Vector<M> sum_top = Zeros;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum_top += diff_delta[t-1][i] * exp(delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]) - Ztj);
diff_delta[t][j] = B.diff_log(j, O[t]) + (sum_top) / sum;
if(compute_hessian)
{
Matrix<M> sum_top2 = Zeros;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum_top2 += exp(delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]) - Ztj) * ( hess_delta[t-1][i] + diff_delta[t-1][i].as_col() * diff_delta[t-1][i].as_row());
hess_delta[t][j] = B.hess_log(j, O[t]) + sum_top2 / sum - sum_top.as_col() * sum_top.as_row() / (sum*sum);
}
}
}
}
//Compute the log prob using normalization
double Z = -HUGE_VAL;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
Z = max(Z, delta.back()[i]);
double sum =0;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum += exp(delta.back()[i] - Z);
double log_prob = Z + ln(sum);
//Compute the differential of the log
Vector<M> diff_log = Zeros;
//Compute the differential of the log using normalization
//The convenient normalizer is ln P(O|lambda) which makes the bottom 1.
for(int i=0; compute_deriv && i < states; i++)
diff_log += exp(delta.back()[i] - log_prob)*diff_delta.back()[i];
Matrix<M> hess_log = Zeros;
//Compute the hessian of the log using normalization
//The convenient normalizer is ln P(O|lambda) which makes the bottom 1.
for(int i=0; compute_hessian && i < states; i++)
hess_log += exp(delta.back()[i] - log_prob) * (hess_delta.back()[i] + diff_delta.back()[i].as_col() * diff_delta.back()[i].as_row());
hess_log -= diff_log.as_col() * diff_log.as_row();
//Compute the differential of the Hessian
return make_tuple(log_prob, diff_log, hess_log);
}
| double forward_algorithm | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| TooN::Vector< States > | pi, | ||
| const Btype & | B, | ||
| const std::vector< Otype > & | O | ||
| ) |
Run the forward algorithm and return the log probability.
- Parameters:
-
A A: State transition probabilities. pi 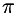 : initial state probabilities.
: initial state probabilities. O O or I: the observed data (ie the images). B 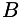 : A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state.
: A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state.
- Returns:
- the log probability of observing all the data.
Definition at line 244 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References ln().
{
using namespace TooN;
using namespace std;
using namespace std::tr1;
int states = pi.size();
//delta[j][i] = delta_t(i)
vector<array<double, States> > delta(O.size());
//Initialization: Eqn 19, P 262
//Set initial partial log probabilities:
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
delta[0][i] = ln(pi[i]) + B.log(i, O[0]);
//Perform the recursion: Eqn 20, P262
//Note, use T and T-1. Rather than T+1 and T.
for(unsigned int t=1; t < O.size(); t++)
{
for(int j=0; j < states; j++)
{
double Ztj = -HUGE_VAL; //This is Z_t(j)
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
Ztj = max(Ztj, delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]));
double sum=0;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum += exp(delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]) - Ztj);
delta[t][j] = B.log(j, O[t]) + Ztj + ln(sum);
}
}
//Compute the log prob using normalization
double Z = -HUGE_VAL;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
Z = max(Z, delta.back()[i]);
double sum =0;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum += exp(delta.back()[i] - Z);
double log_prob = Z + ln(sum);
return log_prob;
}
| std::pair<double, TooN::Vector<Btype::NumParameters> > forward_algorithm_deriv | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| TooN::Vector< States > | pi, | ||
| const Btype & | B, | ||
| const std::vector< Otype > & | O | ||
| ) |
Run the forward algorithm and return the log probability and its derivatives.
- Parameters:
-
A A: State transition probabilities. pi 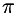 : initial state probabilities.
: initial state probabilities. O O or I: the observed data (ie the images). B 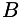 : A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
: A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
- Returns:
- the log probability of observing all the data.
Definition at line 302 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References forward_algorithm_hessian().
Referenced by SpotNegProbabilityDiffWithSampledBackground::operator()().
{
using namespace std::tr1;
double p;
TooN::Vector<Btype::NumParameters> v;
tie(p,v, ignore) = forward_algorithm_hessian(A, pi, B, O, 1, 0);
return make_pair(p,v);
}
| std::vector<std::tr1::array<double, States> > forward_algorithm_delta | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| TooN::Vector< States > | pi, | ||
| const Btype & | B, | ||
| const std::vector< Otype > & | O | ||
| ) |
Run the forward algorithm and return the log partials (delta)
- Parameters:
-
A A: State transition probabilities. pi 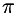 : initial state probabilities.
: initial state probabilities. O O or I: the observed data (ie the images). B 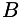 : A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
: A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
- Returns:
- the log probability of observing all the data.
Definition at line 323 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References ln().
Referenced by forward_backward_algorithm(), SampledMultispot::GibbsSampler::next(), and sampled_background_spot_hessian_ffbs().
{
using namespace TooN;
using namespace std;
using namespace std::tr1;
int states = pi.size();
//delta[j][i] = delta_t(i)
vector<array<double, States> > delta(O.size());
//Initialization: Eqn 19, P 262
//Set initial partial log probabilities:
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
delta[0][i] = ln(pi[i]) + B.log(i, O[0]);
//Forward pass...
//Perform the recursion: Eqn 20, P262
//Note, use T and T-1. Rather than T+1 and T.
for(unsigned int t=1; t < O.size(); t++)
{
for(int j=0; j < states; j++)
{
double Ztj = -HUGE_VAL; //This is Z_t(j)
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
Ztj = max(Ztj, delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]));
double sum=0;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum += exp(delta[t-1][i] + ln(A[i][j]) - Ztj);
delta[t][j] = B.log(j, O[t]) + Ztj + ln(sum);
}
}
return delta;
}
| void forward_algorithm_delta2 | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| TooN::Vector< States > | pi, | ||
| const Btype & | B, | ||
| const std::vector< Otype > & | O, | ||
| std::vector< std::tr1::array< double, States > > & | delta | ||
| ) |
Run the forward algorithm and return the log partials (delta)
- Parameters:
-
A A: State transition probabilities. pi 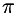 : initial state probabilities.
: initial state probabilities. O O or I: the observed data (ie the images). B 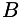 : A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
: A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters. delta the 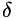 values
values
Definition at line 371 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References ln().
{
using namespace TooN;
using namespace std;
using namespace std::tr1;
int states = pi.size();
//delta[j][i] = delta_t(i)
delta.resize(O.size());
//Initialization: Eqn 19, P 262
//Set initial partial log probabilities:
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
delta[0][i] = ln(pi[i]) + B.log(i, O[0]);
Matrix<States> lA;
for(int r=0; r < States; r++)
for(int c=0; c < States; c++)
lA[r][c] = ln(A[r][c]);
//Forward pass...
//Perform the recursion: Eqn 20, P262
//Note, use T and T-1. Rather than T+1 and T.
for(unsigned int t=1; t < O.size(); t++)
{
for(int j=0; j < states; j++)
{
double Ztj = -HUGE_VAL; //This is Z_t(j)
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
Ztj = max(Ztj, delta[t-1][i] + lA[i][j]);
double sum=0;
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
sum += exp(delta[t-1][i] + lA[i][j] - Ztj);
delta[t][j] = B.log(j, O[t]) + Ztj + ln(sum);
}
}
}
| std::pair<std::vector<std::tr1::array<double, States> >, std::vector<std::tr1::array<double, States> > > forward_backward_algorithm | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| TooN::Vector< States > | pi, | ||
| const Btype & | B, | ||
| const std::vector< Otype > & | O | ||
| ) |
Run the forward-backwards algorithm and return the log partials (delta and epsilon).
- Parameters:
-
A A: State transition probabilities. pi 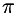 : initial state probabilities.
: initial state probabilities. O O or I: the observed data (ie the images). B 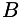 : A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
: A function object giving the (log) probability of an observation given a state, and derivatives with respect to the parameters.
- Returns:
- the log probability of observing all the data.
Backward pass Epsilon is log beta
Definition at line 424 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References forward_algorithm_delta(), and ln().
{
using namespace TooN;
using namespace std;
using namespace std::tr1;
int states = pi.size();
//delta[j][i] = delta_t(i)
vector<array<double, States> > delta = forward_algorithm_delta(A, pi, B, O);
///Backward pass
///Epsilon is log beta
vector<array<double, States> > epsilon(O.size());
//Initialize beta to 1, ie epsilon to 0
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
epsilon[O.size()-1][i] = 0;
//Perform the backwards recursion
for(int t=O.size()-2; t >= 0; t--)
{
for(int i=0; i < states; i++)
{
//Find a normalizing constant
double Z = -HUGE_VAL;
for(int j=0; j < states; j++)
Z = max(Z, ln(A[i][j]) + B.log(j, O[t+1]) + epsilon[t+1][j]);
double sum=0;
for(int j= 0; j < states; j++)
sum += exp(ln(A[i][j]) + B.log(j, O[t+1]) + epsilon[t+1][j] - Z);
epsilon[t][i] = ln(sum) + Z;
}
}
return make_pair(delta, epsilon);
}
| int select_random_element | ( | const A & | v, |
| const double | scale, | ||
| Rng & | rng | ||
| ) |
Select an element from the container v, assuming that v is a probability distribution over elements up to some scale.
- Parameters:
-
v Uscaled probability distribution scale Scale of v rng Random number generator to use
Definition at line 479 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References scale().
Referenced by sample_unscaled_log().
{
double total=0, choice = rng()*scale;
for(int i=0; i < (int)v.size(); i++)
{
total += v[i];
if(choice <= total)
return i;
}
return v.size()-1;
}
| int sample_unscaled_log | ( | std::tr1::array< double, N > | a, |
| Rng & | rng | ||
| ) |
Select an element from the a, assuming that a stores unscaled log probabilities of the elements.
- Parameters:
-
a Uscaled probability distribution, stored as logarithms. rng Random number generator to use
Definition at line 497 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References select_random_element().
{
double hi = *max_element(a.begin(), a.end());
double sum=0;
for(unsigned int i=0; i < a.size(); i++)
{
a[i] = exp(a[i] - hi);
sum += a[i];
}
return select_random_element(a, sum, rng);
}
| std::vector<StateType> backward_sampling | ( | TooN::Matrix< States > | A, |
| const std::vector< std::tr1::array< double, States > > & | delta, | ||
| Rng & | rng | ||
| ) |
An implementation of the backwards sampling part of the forwards filtering/backwards sampling algorithm.
See `Monte Carlo smoothing for non-linear time series', Godsill and Doucet, JASA 2004
- Parameters:
-
A HMM transition matrix. delta Forward partial probabilities stored as logarithms. rng Random number generator to use
- Returns:
- state at each time step.
Definition at line 519 of file forward_algorithm.h.
References ln().
{
//Compute the elementwise log of A
for(int r=0; r < A.num_rows(); r++)
for(int c=0; c < A.num_cols(); c++)
A[r][c] = ln(A[r][c]);
std::vector<StateType> samples(delta.size());
samples.back() = sample_unscaled_log<States, Rng>(delta.back(), rng);
//A is A[t][t+1]
for(int i=delta.size()-2; i >= 0; i--)
{
std::tr1::array<double, States> reverse_probabilities = delta[i];
for(int j=0; j < States; j++)
reverse_probabilities[j] += A[j][samples[i+1]];
samples[i] = sample_unscaled_log<States, Rng>(reverse_probabilities, rng);
}
return samples;
}
 1.7.4
1.7.4